In this little page I will describe how to configure a vpn connection between two different networks. This connection is usually called site2site vpn.
I used ipsectools and recoon projects to establish a vpn tunnel. In Debian distributions, to install required packages we type:
# sudo apt-get install ipsec-tools racoon
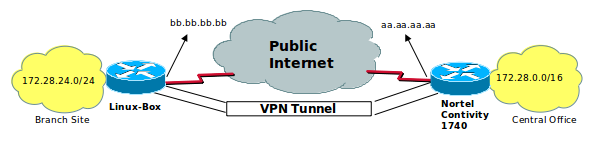
We have to edit some configuration files. I want to explain the related services using the sample configuration. We call Branche Office for the node on the left and central office for the other one. The vpn tunnel is shown in the picture above. The branche office, which is the one we are talking about is a Linux installed machine and the central office is using Nortel Contivity 1740 VPN BOX. The branch office has got 172.28.24.0 / 24 network address. The central office has got 172.28.0.0 / 16 network address. 172.28.0.0 / 16 is for to contain the brache office segment.
But as you know, If you look at from branch office, all other branch offices are behind the central office. So first of all, we have to fix this problem.
The problem is that, if we will define the destination network as 172.28.0.0/16, our vpn box device sends packets through the tunnel interface for accessing to 172.28.24.0 / 24 segment. But 172.28.24.0 / 24 segment is already connected to itself! In this sample, our vpn destination network is 0.0.0.0 / 0. Because, this is a branch office and we want to have full control on internet access requests from the branch office. The spd.conf file (/etc/spd.conf) seems like that;
spdadd 172.28.24.0/24 172.28.24.0/24 any -P in none;
spdadd 172.28.24.0/24 172.28.24.0/24 any -P out none;
spdadd 172.28.24.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 any -P out ipsec ah/tunnel/bb.bb.bb.bb-aa.aa.aa.aa/require;
spdadd 0.0.0.0/0 172.28.24.0/24 any -P in ipsec ah/tunnel/aa.aa.aa.aa-bb.bb.bb.bb/require;
first two lines are required to fix the problem. Last two lines are required to establish vpn tunnel. These are define tunnel source/destination networks and tunnel source/destinatio ends. (aa.aa.aa.aa is ip address of vpn catcher device on the central office and bb.bb.bb.bb is ip address of branch office box. So it is our linux ip address.)
This site to site vpn tunnel is using pre-shared key mechanism. So we need a pre-shared key configuration file. The file seems like that;
aa.aa.aa.aa [pre-shared key]
This file must be located in /etc/racoon directory in our defined system. The other configuration file that located in /etc/rac oon directory is racoon.conf:
listen {
adminsock "/var/run/racoon.sock" "root" "wheel" 0660;
}
path pre_shared_key "/etc/racoon/psk.txt";
path certificate "/etc";
remote aa.aa.aa.aa {
exchange_mode aggressive;
my_identifier fqdn "BranchOfficeName";
peers_identifier address aa.aa.aa.aa;
initial_contact on;
ike_frag on;
support_proxy on;
proposal_check obey;
proposal {
encryption_algorithm 3des;
hash_algorithm md5;
authentication_method pre_shared_key;
dh_group 2;
}
}
sainfo address 172.28.24.0/24 any address 0.0.0.0/0 any {
encryption_algorithm des,3des;
authentication_algorithm hmac_sha1,hmac_md5;
compression_algorithm deflate;
lifetime time 5 min;
pfs_group 2;
}
the racoon.conf file contains this tunnel configuration, source and destionation network addresses and some ipsec option selections. So you can select different encryption options in this file. But the important point is, each ends should have the same selections. bb.bb.bb.bb might be a problem for you if it's changeable. If this ip address is changeable, you have to recognize the current value and you have to update it in /etc/spd.conf file. And then, you have to update it on the running service. You can use setkey command to manage tunnel properties.
setkey -D
setkey -DP
setkey -F
/etc/init.d/setkey {start|stop|restart|force-reload}
-D Dump the SAD entries, -F Flush the SAD entries and /etc/init.d/setkey is initialize shell script.
If you create new spd.conf file in different path, you have to kill existing setkey process (or you can use '/usr/sbin/setkey -F -FP' command) and load new conf file with following command:
kill existing setkey process;
start setkey with new spd.conf file
/usr/sbin/setkey -f /etc/spd.conf

Finally, if your Linux box's public ip address is changable you can sense current ip address on external interface and update spd.conf file with following php script. It reads some informations from racoon.conf file. If you don't need these parts, you can mark the line with "#" to make it commented.
The filename is createSpd.php (full path: /root/fwscripts/createSpd.php):
#!/usr/bin/php
<?php
$k = 0;
$i = 1;
while($k < 5){
$lan = exec("/sbin/ifconfig eth0 | /bin/grep 'inet addr' | /usr/bin/gawk -F ' ' '{print $2}' | /usr/bin/gawk -F ':' '{print $2}'");
$wan = exec("/sbin/ifconfig ppp0 | /bin/grep 'inet addr' | /usr/bin/gawk -F ' ' '{print $2}' | /usr/bin/gawk -F ':' '{print $2}'");
//$peer = 'aa.aa.aa.aa'; // you can use this line or following line.
$peer = exec("/bin/grep remote /etc/racoon/racoon.conf | /usr/bin/gawk -F ' ' '{ print $2 }'");
$localNet = exec("/bin/grep sainfo /etc/racoon/racoon.conf | /usr/bin/gawk -F ' ' '{ print $3 }'");
$remoteNet = exec("/bin/grep sainfo /etc/racoon/racoon.conf | /usr/bin/gawk -F ' ' '{ print $6 }'");
$blan = strlen($lan);
$bwan = strlen($wan);
echo "strlen($lan):$blan,strlen($wan):$bwan \n";
if($blan < "6" || $bwan < "6" ) {
echo "LAN or WAN hasn't got usable ip address.\n";
echo "The script wait and will be try again!!! ($i) # # # # # # # # # # # \n";
$i++;
sleep(10);
} else {
echo "writing to /etc/spd.conf file as collected information:\n";
exec("/bin/rm -rf /etc/spd.conf.old;/bin/mv /etc/spd.conf /etc/spd.conf.old");
exec("echo 'spdadd 172.28.10.254/32 0.0.0.0/0 any -P out none;' > /etc/spd.conf");
exec("echo 'spdadd 0.0.0.0/0 172.28.10.254/32 any -P in none;' >> /etc/spd.conf");
exec("echo 'spdadd $localNet $localNet any -P in none;' >> /etc/spd.conf");
exec("echo 'spdadd $localNet $localNet any -P out none;' >> /etc/spd.conf");
exec("echo 'spdadd $localNet $remoteNet any -P out ipsec ah/tunnel/$wan-$peer/require;' >> /etc/spd.conf");
exec("echo 'spdadd $remoteNet $localNet any -P in ipsec ah/tunnel/$peer-$wan/require;' >> /etc/spd.conf");
$k = 5;
}
if($i > 5){
$k = 7;
}
}
echo "FNSH\n";
?>
If you want to manage the setkey process with a shell script, you can practically use the following script.
#!/bin/sh
case "$1" in
start)
echo "Running ipsec VPN rules file: /etc/spd.conf";
/root/fwscripts/createSpd.php
/usr/sbin/setkey -f /etc/spd.conf
;;
stop)
echo "Remove ipsec VPN rules file: /etc/spd.conf"
/usr/sbin/setkey -F -FP
;;
restart)
echo "Remove ipsec VPN rules file: /etc/spd.conf"
/usr/sbin/setkey -F -FP
echo "Running ipsec VPN rules file: /etc/spd.conf";
/root/fwscripts/createSpd.php
/usr/sbin/setkey -f /etc/spd.conf
;;
*)
echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/setkeyHandle {start|stop|restart}"
;;
esac
exit 0
And then, if you want to add this script to boot progress, you can use update-rc.d command in Debian based Linuxs like following,
# update-rc.d setkeyHandle defaults
Adding system startup for /etc/init.d/setkeyHandle ...
/etc/rc0.d/K20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
/etc/rc1.d/K20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
/etc/rc6.d/K20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
/etc/rc2.d/S20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
/etc/rc3.d/S20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
/etc/rc4.d/S20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
/etc/rc5.d/S20setkeyHandle -> ../init.d/setkeyHandle
If you don't want to use default values, you can define your values in the update-rc.d command like following;
# update-rc.d setkeyHandle start 20 2 3 4 5 . stop 80 0 1 6 .







